Agentic AI vs Regular AI: 15 Key Differences You Must Know
Agentic AI vs regular AI is quickly becoming one of the most important distinctions in today’s technology landscape.
While regular AI—such as chatbots, voice assistants, or recommendation engines—mainly responds to prompts, agentic AI represents a new leap.
These systems act with autonomy, plan multi-step tasks, and adapt intelligently to dynamic situations.
Unlike traditional AI, which is limited to answering questions or executing narrow functions, agentic AI takes initiative, manages workflows, and collaborates across tools.
This shift marks a transition from reactive helpers to proactive digital partners.
To see the difference clearly, the following table highlights 15 key contrasts, grouped into five themes that show how agentic AI is redefining what’s possible.
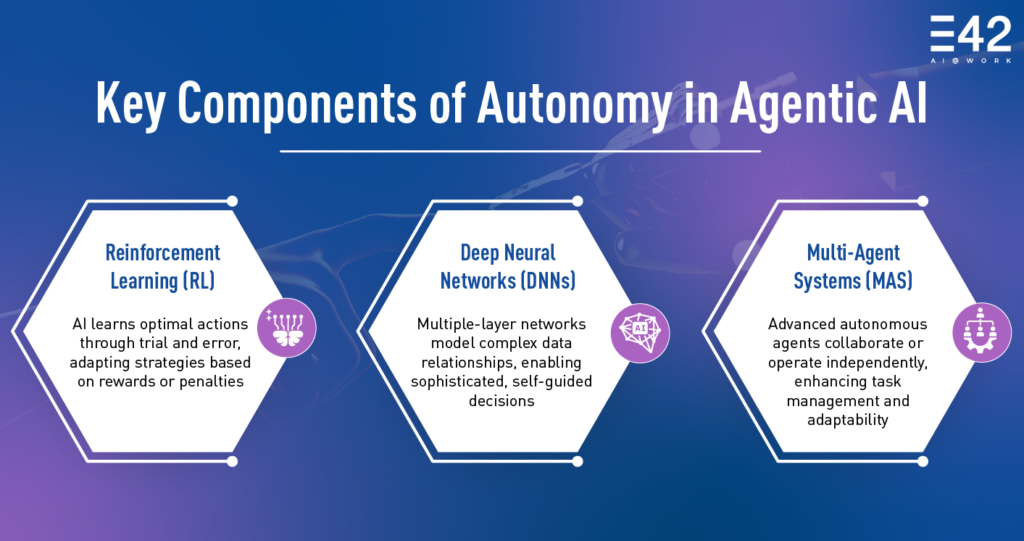
Autonomy and Initiative
Independent Action
Agentic AI sets itself apart by moving beyond mere responses.
It doesn’t wait passively for a human command—it acts according to pre-set objectives and evolving conditions.
Imagine a project management platform where agentic AI automatically assigns tasks to team members based on workload, deadlines, and skill sets.
Source: E42
It doesn’t simply remind you of a due date; it ensures that the task moves forward without your intervention.
In finance, it can flag anomalies, initiate fraud checks, and even draft reports proactively, freeing professionals to focus on decision-making rather than routine monitoring.
Human Reliance in Regular AI
Regular AI, by contrast, remains reactive.
A chatbot won’t independently suggest project steps or adjust task allocations unless specifically prompted.
It answers when you ask, but it does not anticipate needs.
This makes it helpful for straightforward, transactional interactions, but limits its effectiveness in dynamic, fast-changing environments.
Why It Matters
The difference here is more than technical—it’s about redefining the human–machine relationship.
With autonomy, agentic AI becomes a collaborative partner rather than just a tool.
It shoulders routine execution while leaving humans free to think strategically, innovate, and lead.
This marks the beginning of AI as a true co-worker.
Intelligence and Decision-Making
Planning Ability
One of the most striking capabilities of agentic AI is its ability to plan.
Instead of offering fragmented responses, it builds step-by-step workflows that mirror human reasoning.
For instance, during a product launch, agentic AI doesn’t just recommend marketing channels; it organizes the launch sequence—research, content creation, ad scheduling, customer outreach—and ensures every stage follows in the correct order.
This is where the distinction between agentic AI vs regular AI becomes clear: one creates actionable roadmaps, the other only provides scattered advice.
Regular AI Limits
Regular AI remains limited in scope.
A chatbot can tell you the best time to post on social media, but it cannot build a full campaign timeline or adjust tasks when priorities shift.
Source: Era Of Open AI
If a delay arises in design or supply chain, regular AI doesn’t reorganize the plan—it simply waits for another input.
This lack of initiative makes it helpful for narrow tasks but unsuitable for complex, evolving workflows.
The Strategic Leap
This planning ability is the foundation of why businesses are pivoting toward agentic AI.
It merges strategy with execution, allowing organizations to anticipate challenges, adjust dynamically, and achieve outcomes faster.
Ultimately, agentic AI vs regular AI is the leap from reactive advice to proactive orchestration.
15 Differences Between Agentic AI and Regular AI
| Category | Agentic AI | Regular AI / Chatbots |
|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | Acts with minimal supervision, takes initiative to complete multi-step tasks | Needs direct input and instructions for every task |
| Planning | Can design workflows, prioritize tasks, and execute in sequence | Responds to immediate prompts without long-term structure |
| Decision-making | Evaluates multiple options, selects best paths | Relies on pre-set rules or limited algorithms |
| Adaptability | Learns and adjusts in real-time based on new contexts | Struggles to adapt beyond training data |
| Context-awareness | Remembers prior interactions and builds continuity | Often resets after each prompt |
| Goal-orientation | Operates with defined objectives (e.g., “improve efficiency”) | Focuses on answering or assisting without strategic goals |
| Problem-solving | Handles complex, ambiguous scenarios | Excels in structured, repetitive tasks |
| Proactivity | Initiates tasks (e.g., alerts, scheduling) before being asked | Waits for human command to act |
| Collaboration | Can coordinate across systems and tools | Limited to its own environment |
| Scalability | Expands roles in workflows without constant programming | Needs frequent updates for new tasks |
| Human dependency | Reduces manual supervision | Relies heavily on human input |
| Learning style | Employs reinforcement and continuous learning | Dependent on static datasets |
| Risk handling | Assesses and mitigates risks on its own | Leaves risk assessment to humans |
| Execution power | Can close loops (plan → act → review → improve) | Stops after responding or completing single tasks |
| Future-readiness | Designed for evolving enterprise ecosystems | Constrained to narrow, domain-specific uses |
Adaptability and Context
Learning in Real Time
Agentic AI demonstrates a remarkable ability to adapt as situations evolve.
Unlike systems that rely on static rules, it continuously absorbs feedback and updates its behavior in real time.
For example, if a company is running a marketing campaign and consumer sentiment shifts mid-launch, agentic AI can instantly rebalance budgets, redirect messaging, or prioritize new channels without waiting for explicit instructions.
This capacity for learning while acting ensures that goals stay aligned even when the environment changes.
It’s here that the contrast between agentic AI vs regular AI becomes most visible.
Stuck in Place
By comparison, regular AI operates rigidly.
A chatbot can answer frequently asked questions but struggles when faced with ambiguity.
Source: AD Device
If an unexpected issue arises—say a sudden supply chain disruption—it cannot re-plan logistics or adapt strategies on its own.
Instead, it halts or provides generic responses until a human intervenes.
This inability to handle shifting variables makes regular AI reactive, not resilient.
Long-Term Advantage
Adaptability isn’t just a technical bonus—it’s a long-term competitive edge.
Industries like finance, healthcare, and e-commerce demand constant responsiveness.
Agentic AI thrives in these environments, ensuring organizations can pivot quickly.
In the contest of agentic AI vs regular AI, adaptability decides who survives disruption and who lags behind.
Proactivity and Collaboration
Taking the First Step
One of the defining strengths of agentic AI is its ability to take initiative.
Instead of waiting passively for a command, it steps in proactively to reduce risks and improve efficiency.
Imagine a project management system where the AI automatically reminds you of potential bottlenecks, reschedules delayed tasks, or alerts stakeholders before an issue becomes critical.
This is where the debate of agentic AI vs regular AI becomes clear—one anticipates problems and acts early, the other waits to be told.
Working Together
Agentic AI also excels at collaboration across platforms.
It doesn’t just operate within a single tool; it integrates seamlessly across CRM systems, HR software, analytics dashboards, and communication channels.
For instance, an agentic AI can pull customer insights from Salesforce, sync deadlines with Slack, and update HR availability in real time—functioning as a true coordinator that bridges silos.
This interconnectedness makes workflows smoother and decision-making faster.
Reactive Role of Regular AI
In contrast, regular AI tools remain confined to narrow environments.
A chatbot may perform well in customer support but cannot coordinate with other systems or anticipate cross-departmental needs.
Its role stays reactive and siloed, limiting overall impact.
In today’s connected enterprises, the agentic AI vs regular AI divide shows up most sharply in collaboration—only one acts like a team player.
Future-Readiness and Risk Management
Forward-Looking Design
Agentic AI is not just about solving today’s problems—it is engineered for tomorrow’s challenges.
Built with adaptability in mind, it thrives in evolving ecosystems where tools, workflows, and markets are constantly changing.

Source: AI Tech Toolbox
For example, as enterprises adopt new platforms or expand into fresh markets, agentic AI adjusts its processes seamlessly, ensuring continuity without disruption.
This future-ready design means organizations can innovate confidently, knowing their AI systems will grow alongside them.
Handling Risks
Another critical strength of agentic AI is its capacity for proactive risk management.
It doesn’t simply detect errors after they happen—it evaluates potential scenarios in advance, prevents mistakes, and suggests mitigation steps.
In healthcare, this could mean identifying patient risks before emergencies arise; in finance, flagging fraud before losses occur.
The contrast between agentic AI vs regular AI is stark here: one anticipates danger, the other only reacts when the issue is already visible.
Why Regular AI Lags
Regular AI, including chatbots, remains narrow by design.
While still useful for specific functions, it cannot orchestrate enterprise-wide strategies or evolve with complex environments.
This limitation highlights the true difference in agentic AI vs regular AI—only agentic systems combine foresight, resilience, and adaptability to prepare organizations for an uncertain future.
FAQs
1. What is the core difference between agentic AI and chatbots?
Agentic AI acts independently with planning and initiative, while chatbots simply respond to commands.
2. Can agentic AI fully replace humans?
No, it complements humans by automating workflows and freeing people for higher-level strategy.
3. Is agentic AI always better than regular AI?
Not necessarily. Regular AI is perfect for simple, repetitive tasks, while agentic AI fits complex, dynamic scenarios.
4. Which industries benefit most from agentic AI?
Industries like healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and broadcasting gain from its adaptability and proactive features.
5. Does agentic AI require more resources to implement?
Yes, it often needs deeper integration and stronger data pipelines, but the payoff in efficiency is higher.
6. How can small businesses use agentic AI?
Even small firms can apply it for task automation, scheduling, and adaptive customer service.
Related Posts
10 Real-World Agentic AI Examples You Should Know
See how agentic AI is already transforming industries with autonomy and adaptability. These examples show the shift from theory to reality.
Are AI Agents Replacing You? Here’s What You Must Know
AI agents are moving beyond assistance into execution. Understand what this means for your role, opportunities, and survival.
AI Threat Lies in Indifference, Not Killer Robots
The real risk isn’t sci-fi machines but human neglect in governing AI. Indifference could cause more damage than aggression.
10 Real-World Agentic AI Examples You Should Know
From healthcare to finance, discover practical cases where agentic AI acts proactively. These examples reveal its true power and scope.
Conclusion
Agentic AI represents a paradigm shift.
Where regular AI helps in limited, reactive ways, agentic systems take on broader responsibilities—planning, acting, adapting, and collaborating.
They transform AI from a helper into an autonomous partner in achieving goals.
As industries evolve, the gap between regular and agentic AI will widen. Those who embrace the agentic model will gain agility, efficiency, and resilience, while those stuck with basic tools risk falling behind.

