Data Privacy in Digital Marketing: Protecting Your Digital Privacy
In the fast-paced world of digital marketing, the most important concern is “data privacy.”
As businesses navigate the complex world of online promotion, protecting user information takes precedence to ensure trust and compliance with changing rules.
For instance, picture this: 8 out of 10 people are side-eyeing their screens, worried about who’s peeking at their online secrets.
So what exactly is data privacy in digital marketing?
In a privacy-focused world, today digital marketers are rapidly adapting. Instead of mass data collection, they selectively gather only crucial data that is needed. This is boosting customer trust and hence encouraging their return.
We’re now diving into the wild world of data privacy in digital marketing, where things get real. It’s not just about jargon-filled legalities.
Rather, it’s about keeping it cool and respecting the boundaries. Because, let’s face it, we all want our info to be treated like VIPs.
In this article, we’re tackling the real talk—why your online privacy matters, the hiccups businesses face, and how we can all play nice in this digital playground of rules and regs.
Are you ready to decode the buzz around data privacy?
Let’s roll!
1. The Evolving Landscape of Data Privacy Regulations
In the ever-evolving world of digital marketing, staying in the loop on data privacy regulations is like navigating a constantly changing maze.
So who are the major players shaping this landscape globally? Let’s see.
1.1. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
According to Search Engine Journal “The General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR as it is known, requires that users explicitly opt into tracking and gives them a choice about how they can be tracked after they opt in“
- Enacted in 2018, the GDPR is the European Union’s heavyweight data protection champion.
- Key Principles:
- Lawful Processing: Data must be processed legally and transparently.
- Purpose Limitation: Collected data must have a specific, legitimate purpose.
- Data Minimization: Only the necessary data should be processed for the intended purpose.
- Accuracy: Data should be accurate and up-to-date.
- Requirements:
- Consent: Explicit consent is required for data processing.
- Data Subject Rights: Individuals have the right to access and control their data.
- Data Breach Notification: Prompt reporting of data breaches is mandatory.
Here’s what Robert Baugh (Founder &CEO of Keepabl) says about GDPR in Privacy Kitchen.
1.2. CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)
As per the official website of California Govt. “Businesses that are subject to the CCPA have several responsibilities, including responding to consumer requests to exercise these rights and giving consumers certain notices explaining their privacy practices. The CCPA applies to many businesses, including data brokers“
- Enacted in 2020, the CCPA is California’s response to the growing need for consumer data protection.
- Key Principles:
- Consumer Rights: Californian residents have the right to know, delete, and opt out of the sale of their personal information.
- Business Obligations: Companies must disclose data practices and implement security measures.
- Requirements:
- Data Transparency: Businesses must inform consumers about the categories of data collected.
- Opt-Out Rights: Consumers can opt out of the sale of their data.
- Non-Discrimination: Businesses cannot discriminate against consumers who exercise their privacy rights.
1.3. Other Relevant Regional Regulations
- LGPD in Brazil:
- Enacted in 2020, the LGPD (Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados) emphasizes the lawful processing of personal data and grants individuals control over their information.
- PDPB in India:
- Still, in the legislative pipeline, the PDPB (Personal Data Protection Bill) aims to safeguard the privacy of Indian citizens by regulating the processing of personal data.
1.4. Exploring the Common Threads
- Despite regional nuances, these regulations share common core principles like the emphasis on user consent, transparent data processing practices, and robust security measures.
- Businesses operating globally must weave these principles into their data strategies to ensure compliance and build trust in the digital marketplace.
As we navigate the intricacies of these regulations, it’s clear that a global approach to data privacy is emerging.
It is also urging businesses to adapt and prioritize consumer data protection on a universal scale.
Let’s now see how privacy regulations have impacted digital marketing practices globally.
2. Impact on Digital Marketing Practices
It’s important to note that privacy regulations caused a significant shift in how businesses navigate the world of digital marketing.
Let’s dive into how businesses are navigating these waters, and why the era of “click first, ask questions later” is making way for a more consensual and transparent approach.
2.1. Strategic Shifts in Data Collection:
- From Mass Harvesting to Targeted Precision: Before regulations tightened their grip, collecting data en masse was the norm. Now, businesses are recalibrating to focus on targeted data collection, ensuring they gather only what’s necessary for personalized marketing without infringing on privacy boundaries.
- Embracing Ethical Data Practices: Ethical considerations are taking center stage. Marketers are moving away from exploitative data practices to foster trust, understanding that customer loyalty is built on a foundation of respect for their privacy.
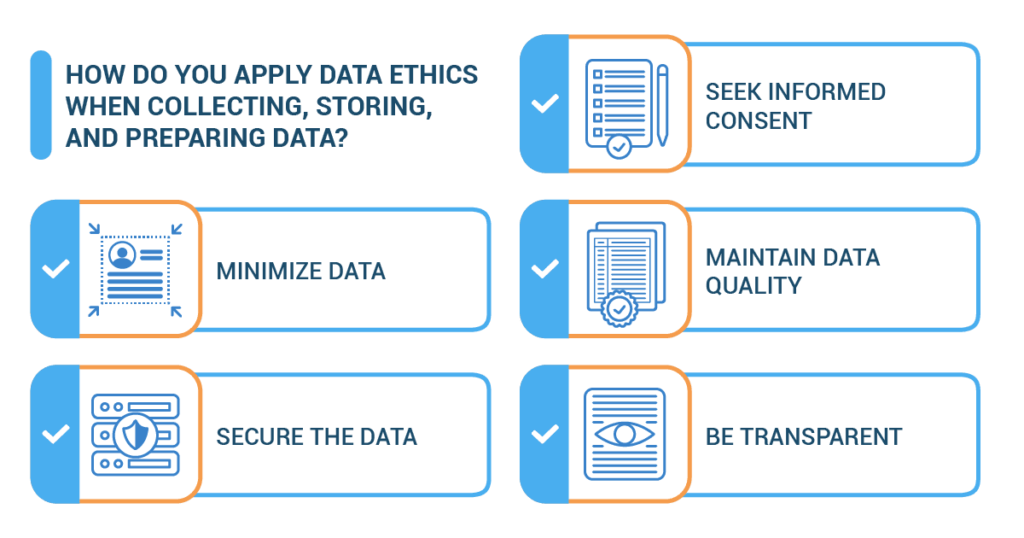
2.2. The Power of Explicit User Consent:
- Gone are the Ambiguous Agreements: With regulations like GDPR and CCPA, vague terms and conditions are no longer cutting it. Explicit user consent is the new currency, with consumers being informed about what data is being collected, why, and how it will be used.
- Opt-In Becomes the Norm: The era of default opt-ins is waning. Marketers recognize the importance of clear and affirmative opt-ins, ensuring users actively agree to their data being processed.
2.3. Transparency as the Cornerstone:
- Consumer Trust Hinges on Transparency: Transparency isn’t just a buzzword; it’s the lifeline of digital marketing post-regulations. Brands that openly communicate their data practices, detailing the ‘what, why, and how‘ to consumers, are earning trust in a landscape where trust is currency.
Here’s what UNCTAD says about data privacy and transparency in the digital economy:
- Educating Consumers on Data Usage: Marketers are taking on the role of educators, explaining to consumers how their data powers a personalized online experience. This transparency is a regulatory requirement and strategic move to build long-lasting relationships.
2.4. Challenges and Opportunities:
Navigating the Personalization Paradox:
Striking a balance between personalized marketing and privacy is the new challenge. Smart marketers are finding innovative ways to deliver tailored experiences without compromising user trust.
Data as a Differentiator:
In a sea of businesses, those that champion data privacy are standing out.
For savvy marketers, respecting user privacy isn’t just compliance; it’s a powerful marketing tool that sets them apart from competitors.
In this era of heightened privacy consciousness, digital marketers are rewriting the playbook.
It’s no longer just about clicks and conversions.
Rather, it’s about building relationships founded on trust, transparency, and the mutual exchange of value between businesses and consumers.
As we journey deeper into the digital age, the companies that prioritize privacy are the ones set to thrive.
Eventually, these privacy regulations become a challenge to marketers and businesses.
That’s why, as a digital marketer you need to know what you can do to overcome them.
3. Challenges Faced by Marketers
Navigating the landscape of data privacy regulations isn’t a stroll in the park for digital marketers.
As they strive to align with evolving standards, a host of challenges arise. They demand a delicate balance between delivering personalized experiences, and respecting user privacy.
3.1. Data Handling Complexity:
- Challenge:
- Managing the intricate web of data sources, ensuring compliance with diverse regulations, and maintaining data accuracy can be an operational puzzle.
- Resolution:
- Implementing robust data governance frameworks and leveraging advanced tools for data management can streamline processes and reduce the risk of non-compliance.

3.2. Consent Conundrum:
- Challenge:
- Obtaining unambiguous user consent can be tricky. Ambiguous opt-ins and complex legalese can lead to compliance pitfalls.
- Resolution:
- Simplifying consent processes, using plain language, and employing user-friendly interfaces can encourage active and informed opt-ins.
3.3. Third-Party Dilemmas:
- Challenge:
- Relying on third-party vendors and partners for data processing introduces a layer of complexity in ensuring that all entities in the data chain uphold privacy standards.
- Resolution:
- Conducting thorough vendor assessments, incorporating stringent contractual clauses, and regularly auditing third-party practices can mitigate risks associated with external dependencies.
3.4. Personalization vs. Privacy Balancing Act:
- Challenge:
- Striking the right balance between personalized marketing and user privacy is a perpetual tightrope walk. Overly aggressive personalization may encroach on privacy boundaries.
- Resolution:
- Leveraging anonymized data, employing AI-driven algorithms that respect privacy preferences, and providing users with granular control over their data can help strike a harmonious balance.
3.5. Global Compliance Juggling:
- Challenge:
- Operating on a global scale means contending with a patchwork of regional regulations, each with its own nuances and requirements.
- Resolution:
- Adopting a proactive approach by staying abreast of evolving regulations, investing in legal counsel, and implementing flexible systems that can adapt to diverse compliance landscapes.
3.6. Building a Privacy-Centric Culture:
- Challenge:
- Shifting organizational culture towards prioritizing privacy can be met with resistance and requires continuous education and advocacy.
- Resolution:
- Incorporating privacy awareness training, appointing dedicated privacy officers, and fostering a company-wide commitment to ethical data practices can instill a culture of privacy.
In the face of these challenges, digital marketers are not merely responders but architects of solutions.
By embracing a proactive and user-centric mindset, you can transform challenges into opportunities. This in turn builds trust and loyalty in an era where data privacy is non-negotiable.
As the digital marketing landscape evolves, so too must the strategies employed to safeguard user privacy. And all this while you need to keep delivering personalized and relevant content.
Keep reading to learn how you can ensure data privacy without compromising on your marketing strategies.
4. Best Practices for Data Privacy in Digital Marketing
In digital marketing, ensuring data privacy compliance is not just a legal necessity—it’s a commitment to building trust with your audience.
Here are actionable tips for marketers to enhance data privacy and navigate the complex web of regulations:
4.1. Consent Management:
Clear and Concise Communication:
Ensure that privacy policies and consent requests are written in plain language, making it easy for users to understand the implications of data collection.
Granular Consent Options:
Give users the ability to offer specific consents for different types of data processing. It empowers users to control how their information is used.
Opt-In, Not Opt-Out:
Make opt-in the default setting rather than opt-out. Users should actively agree to the collection and use of their data, promoting transparency and consent.
Preference Centers:
Implement preference centers where users can easily manage their consents, providing a user-friendly interface for adjusting privacy settings.
4.2. Data Encryption and Security Measures:
- Implement End-to-End Encryption: Ensure that all sensitive data is encrypted from the moment it’s collected until it’s stored and processed. It protects user information from unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct periodic security audits to identify vulnerabilities and address potential risks. This proactive approach helps in maintaining a robust security posture.
- Tokenization for Payment Data: If handling payment information, consider tokenizing sensitive data to replace it with a unique identifier. It reduces the risk associated with storing financial information.
- Secure Data Transmission: Use secure protocols (such as HTTPS) to encrypt data during transmission between the user’s browser and your servers, preventing interception by third parties.
4.3. Regular Audits and Assessments:
- Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIA): Conduct DPIAs to evaluate the impact of data processing activities on user privacy. This systematic assessment helps identify and mitigate potential risks.
- Internal Audits: Establish a schedule for internal audits to ensure ongoing compliance with data privacy regulations. Regular reviews help identify and rectify issues before they become major problems.
- External Audits: Engage third-party experts for external audits. Independent assessments can provide an unbiased evaluation of your data privacy practices.
- Continuous Employee Training: Keep your team well-informed about the latest developments in data privacy. Regular training sessions ensure that everyone understands their role in maintaining compliance.
By incorporating these best practices into your digital marketing strategies, you adhere to data privacy regulations and demonstrate a commitment to ethical and responsible use of user information.

In a digital landscape where trust is paramount, these actions can set your brand apart and foster long-lasting relationships with your audience.
Let’s get a peek into how the privacy regulations affected some of the marketing giants in the industry in the upcoming section.
5. Case Studies: Navigating Data Privacy Regulations
The best way to understand the implications of data privacy and their significance on your business is to learn from Real-world examples.
Let’s explore the positive and negative instances in the upcoming section.
5.1. Positive Instances:
Apple’s Privacy Focus:
- Approach: Apple has been a trailblazer in prioritizing user privacy. With features like App Tracking Transparency, users are empowered to control which apps can track their activity.
- Lesson Learned: Prioritizing user privacy can be a market differentiator, fostering trust and brand loyalty.
5.2. Negative Instances:
Facebook’s Cambridge Analytica Scandal:
- Incident: Facebook faced a severe backlash for the unauthorized harvesting of user data by Cambridge Analytica. The incident highlighted the risks of lax data-sharing practices.
- Lesson Learned: Failing to secure user data can lead to a severe erosion of trust, reputational damage, and regulatory scrutiny.
Learning from positive and negative case studies is vital when you’re striving to navigate the complex landscape of data privacy regulations.
The lessons learned from these cases should serve as beacons guiding companies toward a future where data privacy is not just a compliance checkbox but an integral part of ethical business conduct.
FAQs
1. What exactly does data privacy mean in digital marketing?
Data privacy in digital marketing is the responsible and ethical handling of personal information gathered from consumers and website users. This involves safeguarding personal information against illegal access, use, or release.
2. What are the different types of data privacy ?
- Privacy of the Individual: This relates to bodily autonomy, ensuring individuals have control over their personal information.
- Privacy of Behavior and Action: Protecting individuals from unwarranted scrutiny regarding their actions and behavior.
- Privacy of Communication: Safeguarding the confidentiality of personal communication, both online and offline.
- Privacy of Personal Data: Ensuring the security and proper handling of an individual’s personal information.
- Privacy of Thoughts and Feelings: Protecting the confidentiality of one’s thoughts, emotions, and private expressions.
- Privacy of Location and Space: Preserving the confidentiality of an individual’s physical location and personal space.
- Privacy of Association: Protecting the right to freely associate with others without unwarranted intrusion or surveillance.
3. How do marketers obtain permission to use people’s information while following rules and ensuring customer satisfaction?
Marketers ask for permission to use people’s information by following rules and making sure customers are happy. They explain clearly how they’ll use the data, making it easy for people to say yes. This helps build trust and keeps everyone happy in the world of data privacy.
4. What problems do marketers face when dealing with rules about keeping information private?
Marketers have a tough time following rules to keep information private. The rules change, and it’s tricky to use data for advertising while respecting people’s privacy. It’s like a puzzle they have to solve to make sure everything is fair and everyone’s information stays safe.
5. How do other regional data privacy regulations complement or differ from GDPR and CCPA?
Regional data privacy regulations may be similar to GDPR and CCPA, emphasizing user rights and transparent data handling. However, they can also have unique rules based on local needs. Finding a balance between global standards and regional differences is essential for businesses navigating data privacy regulations.
6. How are digital marketing strategies shifting in response to evolving data collection regulations?
Digital marketing strategies are changing because of new rules about collecting data. Now, marketers are being more careful and only gathering the important information. They want to follow the rules and make sure people feel safe while still making their ads interesting and helpful.
Related Posts
Best Ways to Improve Your Social Media Strategy
Does Digital Marketing Really Work For Creating Wealth?
Digital Marketing Secrets: And How To Succeed At Personal Branding
Conclusion
In this dynamic environment, where every click and tap contributes to an intricate digital narrative, the lessons are simple.
Prioritizing data privacy is not merely about avoiding penalties.
It is about embracing a fundamental shift in how businesses approach their relationship with consumers. This also means accepting the inherent value of user trust and safeguarding it as a prized asset.
With this, I conclude this exploration into data privacy in digital marketing.
The takeaways are profound. Strive for transparency, champion proactive compliance, empower users with control over their data, and uphold ethical data practices.
In doing so, businesses not only navigate the complexities of regulations but also set sail on a course toward sustainable success in the digital age.

